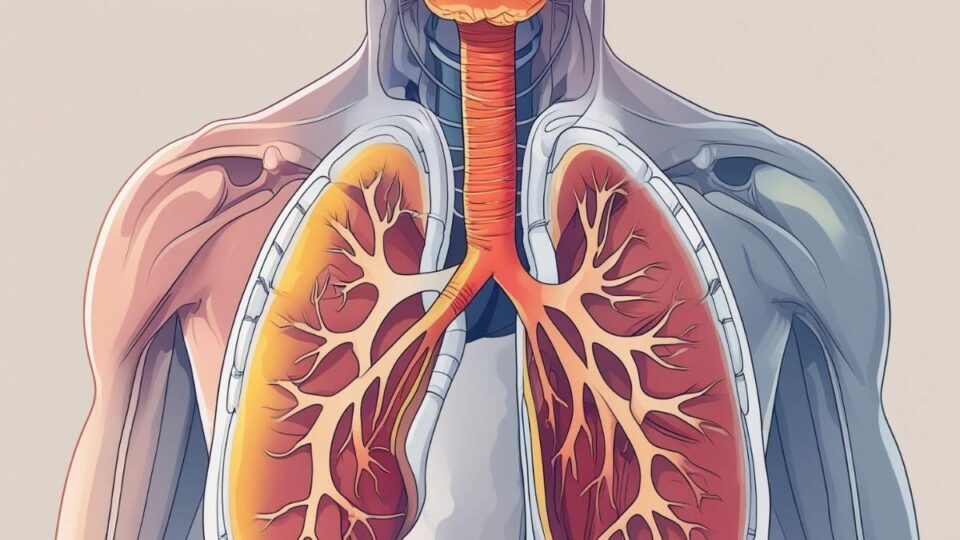
Bronchitis is one of the most common respiratory illnesses worldwide. When it develops with fever, doctors often call it fiebrige bronchitis (which translates to “bronchitis” in English). This condition can be uncomfortable, worrying, and confusing for many patients. Understanding what it is, why it happens, and how it can be treated is key to managing it effectively.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about fiebrige bronchitis, including symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention. Let’s dive in step by step in a simple and clear way.
What Is Fiebrige Bronchitis?
Fiebrige bronchitis is a type of acute bronchitis that comes with fever. Bronchitis itself means inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air into your lungs. When these tubes swell and fill with mucus, it becomes hard to breathe and leads to coughing.
The added fever in fiebrige bronchitis usually signals that your body is fighting an infection, often viral, and sometimes bacterial.
Main Symptoms of Fiebrige Bronchitis
People with this condition usually experience:
- Persistent cough (dry at first, later with mucus)
- Fever (usually low to moderate, but sometimes higher in bacterial cases)
- Chest tightness or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing sounds while breathing
- Fatigue and body aches
If the fever is very high or symptoms worsen after a few days, it may point to a more serious infection, like pneumonia, which needs quick medical attention.
Causes and Risk Factors
The main causes of fiebrige bronchitis are:
- Viral infections – Most cases are triggered by viruses, such as influenza, rhinovirus, or coronavirus.
- Bacterial infections – Less common, but more severe and often require antibiotics.
- Irritants – Cigarette smoke, air pollution, or workplace chemicals can increase the risk.
- Weakened immune system – Children, elderly people, and those with chronic illnesses are more vulnerable.
Risk factors include smoking, frequent colds, asthma, and exposure to dust or fumes.
Diagnosis of Fiebrige Bronchitis
Doctors diagnose fiebrige bronchitis based on:
- Medical history and symptoms
- Physical exam (listening to the lungs with a stethoscope)
- Sometimes, a chest X-ray to rule out pneumonia
- Blood tests if a bacterial infection is suspected
Treatment Options for Bronchitis
Treatment depends on whether the infection is viral or bacterial.
1. For Viral Infections
- Rest and hydration
- Warm fluids like soups and teas
- Over-the-counter pain relievers for fever (e.g., ibuprofen or acetaminophen)
- Cough syrups (in some cases)
- Humidifier use to ease breathing
2. For Bacterial Infections
- Antibiotics prescribed by a doctor
- Symptom management (as above)
3. Supportive Care
- Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke
- Take deep-breathing exercises to clear mucus
- Inhalers may be prescribed for wheezing or asthma patients
Prevention Tips
You can lower the risk of fiebrige bronchitis by:
- Washing hands often to avoid viruses
- Getting flu and pneumonia vaccines
- Wearing masks in polluted or smoky environments
- Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke
- Strengthening immunity through a balanced diet, sleep, and exercise
Difference Between Simple Bronchitis
| Type | Symptoms Without Fever | Symptoms With Fever | Severity Level |
| Acute Bronchitis | Cough, mucus, fatigue | Usually no fever | Mild to moderate |
| Fiebrige Bronchitis | Cough, mucus, fatigue | Fever present | Moderate to severe |
Final Thoughts
Fiebrige bronchitis can be uncomfortable, but in most cases, it is not life-threatening if treated early. The key difference from regular bronchitis is the presence of fever, which should not be ignored. If symptoms last longer than two weeks, or if you have a high fever and chest pain, visiting a healthcare professional is essential.
By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment, you can take the right steps to recover quickly and prevent complications.
FAQs
Q1: Is bronchitis contagious?
Yes, if it is caused by a virus or bacteria, it can spread through coughing, sneezing, or touching contaminated surfaces.
Q2: How long does bronchitis last?
Most cases improve within 1–3 weeks, but cough may linger for a bit longer.
Q3: Can bronchitis turn into pneumonia?
Yes, if untreated or if the immune system is weak, it can develop into pneumonia.
Q4: Do I always need antibiotics for bronchitis?
No, antibiotics are only needed for bacterial infections. Viral cases usually heal with rest and home care.
Q5: When should I see a doctor?
Seek medical help if you have a high fever (above 39°C/102°F), severe chest pain, or difficulty breathing.